
| Origin of transfer (oriT) |
|
The conjugative regions of the self-transmissible MGE typically consist of four modules:
origin of transfer site (oriT), relaxase gene, gene encoding type IV coupling protein (T4CP)
and gene cluster for bacterial type IV secretion system (T4SS).
In general, the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) conjugation process is initiated by relaxase precisely
binding and cleaving the oriT region
[Llosa et al (2002) Mol Microbiol].
After rolling-circle replication, the ssDNA is recruited by T4CP and subsequently transferred
from the donor cell into the recipient cell via T4SS. In addition, non-conjugative MGE
carrying oriT sequences can be mobilized by conjugative elements
(Ramsay et al., Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2017).
The oriT region, usually tens to even hundreds of base pairs in length, contains a conserved nick region (nic) and pairs of inverted repeats (IRs) (De La Cruz et al., FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2009). The nic site is precisely recognized and cleaved by relaxase [de la Cruz, et al (2010) FEMS Microbiol Rev]. |
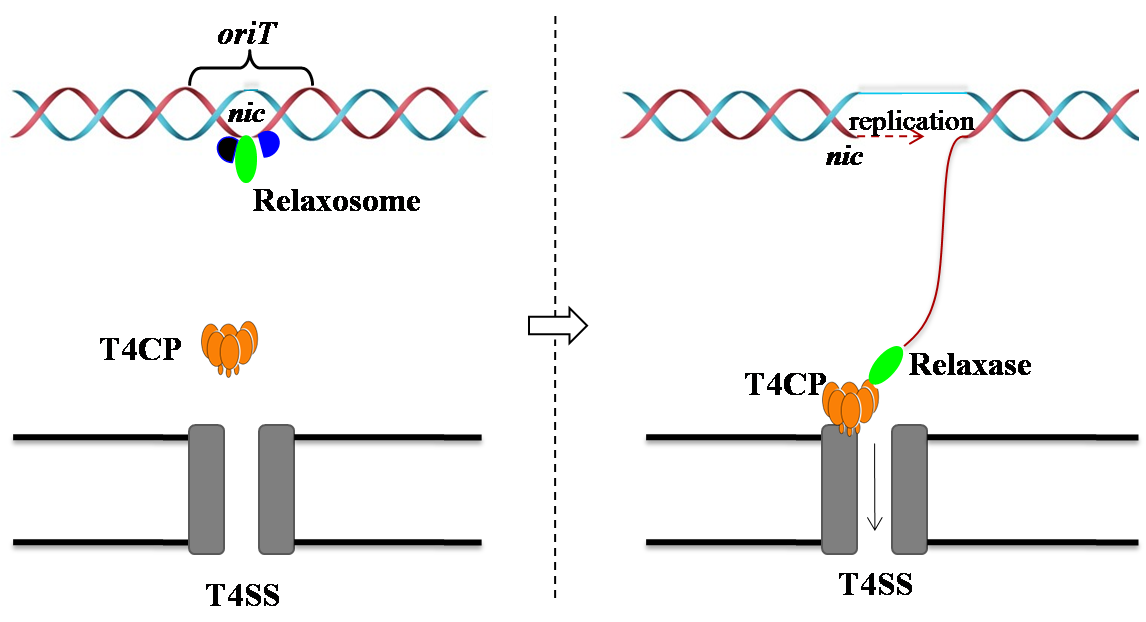
Figure 1. Four modules of the typical self-transmissible MGE: origin of transfer site (oriT), relaxase gene, gene encoding type IV coupling protein (T4CP) and gene cluster for bacterial type IV secretion system (T4SS). |
| oriTfinder: a web-based tool for the identification of origin of transfers in DNA sequences of bacterial mobile genetic elements |
|
oriTfinder was designed to facilitate rapid detection of oriTs in bacterial MGE sequences,
especially in the antimicrobial-resistant plasmids and the virulence plasmids.
The utilized backend database
To evaluate the algorithm, 43 transferable plasmids with experimental supports were used as |
 Figure 2. The prediction strategy used by oriTfinder to identify oriT region. |
| Detection the putative oriT regions with the DNA sequence similarity by using BLASTn-based H-value. |
|
To examine the degree of sequence similarities at a nucleotide level between the
oriTDB-collected oriT sequence and the submitted MGE sequence, oriTfinder employed an
NCBI BLASTn-based H-value with a slight modification. For each query, the H-value was
calculated as follows:
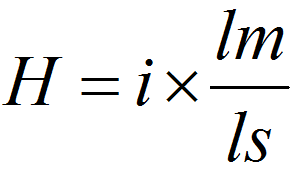 |
| Detection the putative virulence factors (VFs) and acquired antibiotic resistance determinants (ARs) with the protein sequence similarity by using BLASTp-based Ha-value. |
|
To examine the degree of sequence similarities at an amino acid level between each query protein and the oriTfinder-collected
VFs and ARs, the NCBI BLASTp-derived Ha-value was employed. For each query, the Ha-value was calculated as follows:
 |